Thick-film printing Ceramic Substrate (TPC) is to coat the metal paste on the ceramic substrate by screen printing, and then sinter at high temperature (generally 850°C ~ 900°C) to prepare the TPC substrate after drying.
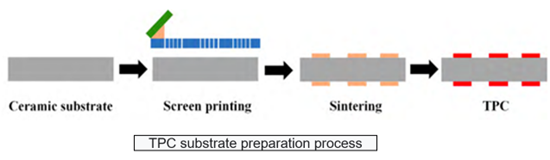 The TFC substrate has a simple preparation process, low requirements for processing equipment and environment, and has the advantages of high production efficiency and low manufacturing cost. The disadvantage is that due to the limitation of the screen printing process, the TFC substrate cannot obtain high-precision lines (Min. line width/line spacing > 100 μm). Depending on the viscosity of the metal paste and the mesh size of the mesh, the thickness of the prepared metal circuit layer is generally 10 μm ~ 20 μm. If you want to increase the thickness of the metal layer, it can be achieved by multiple screen printing. In order to reduce the sintering temperature and improve the bonding strength between the metal layer and the ceramic substrate, a small amount of glass phase is usually added to the metal paste, which will reduce the electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity of the metal layer. Therefore, TPC substrates are only used in the packaging of electronic devices (such as automotive electronics) that do not require high circuit accuracy.
The TFC substrate has a simple preparation process, low requirements for processing equipment and environment, and has the advantages of high production efficiency and low manufacturing cost. The disadvantage is that due to the limitation of the screen printing process, the TFC substrate cannot obtain high-precision lines (Min. line width/line spacing > 100 μm). Depending on the viscosity of the metal paste and the mesh size of the mesh, the thickness of the prepared metal circuit layer is generally 10 μm ~ 20 μm. If you want to increase the thickness of the metal layer, it can be achieved by multiple screen printing. In order to reduce the sintering temperature and improve the bonding strength between the metal layer and the ceramic substrate, a small amount of glass phase is usually added to the metal paste, which will reduce the electrical conductivity and thermal conductivity of the metal layer. Therefore, TPC substrates are only used in the packaging of electronic devices (such as automotive electronics) that do not require high circuit accuracy.
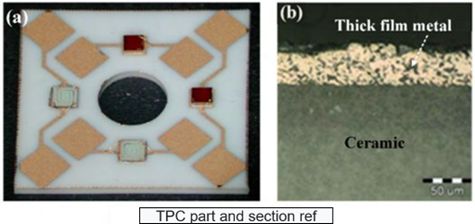 The key technology of TPC substrate lies in the preparation of high-performance metal paste. The metal paste is mainly composed of metal powder, organic carrier and glass powder. The available conductor metals in the paste are Au, Ag, Ni, Cu, and Al. Silver-based conductive pastes are widely used (accounting for more than 80% of the metal paste market) due to their high electrical and thermal conductivity and relatively low price. The research shows that the particle size and morphology of the silver particles have a great influence on the performance of the conductive layer, and the resistivity of the metal layer decreases as the size of the spherical silver particles decreases.
The key technology of TPC substrate lies in the preparation of high-performance metal paste. The metal paste is mainly composed of metal powder, organic carrier and glass powder. The available conductor metals in the paste are Au, Ag, Ni, Cu, and Al. Silver-based conductive pastes are widely used (accounting for more than 80% of the metal paste market) due to their high electrical and thermal conductivity and relatively low price. The research shows that the particle size and morphology of the silver particles have a great influence on the performance of the conductive layer, and the resistivity of the metal layer decreases as the size of the spherical silver particles decreases.
The organic carrier in the metal paste determines the fluidity, wettability and bonding strength of the paste, which directly affects the quality of screen printing and the compactness and conductivity of the later sintered film. Adding glass frit can reduce the sintering temperature of metal paste, reduce production cost and substrate stress.
